[2025-jun-17] The SlackDocs Wiki has moved to a new server, in order to make it more performant.
Table of Contents
Virtual Mail Server Database
This page is supplemental to main article: Creating a Virtual Mail Server with Postfix, Dovecot and MySQL
The database is used to provide configuration and authentication for your virtual mail domains and mail boxes. Email content is not stored in the database in this configuration.
If you have a full Slackware installation with MySQL already working then you may skip to the next section.
If you need to install MySQL (MariaDB) then grab the package and sigfile from a repo, verify it, then install it:
# For 32 bit package #
wget http://slackware.osuosl.org/slackware-14.1/patches/packages/mariadb-5.5.40-i486-2_slack14.1.txz
wget http://slackware.osuosl.org/slackware-14.1/patches/packages/mariadb-5.5.40-i486-2_slack14.1.txz.asc
# For 64 bit package #
wget http://slackware.osuosl.org/slackware64-14.1/patches/packages/mariadb-5.5.40-x86_64-2_slack14.1.txz
wget http://slackware.osuosl.org/slackware64-14.1/patches/packages/mariadb-5.5.40-x86_64-2_slack14.1.txz.asc
gpg --verify mariadb-5.5.40...txz.asc {path to your downloaded package sigfile}
installpkg mariadb-5.5.40...txz
You will then need to initialize the database server and start it. Follow the instructions found in the top comments of the start script, /etc/rc.d/rc.mysqld. Here is a short summary…
mysql_install_db --user=mysql ... chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.mysqld /etc/rc.d/rc.mysqld start ... mysql_secure_installation
Creating Mail DB User and Database
Your database server should now be running and have a root mysql user password set.
Next we need to create a database, and a user to access it on behalf of our mail server.
We will use the highly original names mailserver for our database, and mailuser for our user.
You may easily create both as follows, as root (provide the root mysql user password when prompted):
mysql -p -e "CREATE DATABASE mailserver" mysql -p -e "GRANT ALL ON mailserver.* TO mailuser@localhost IDENTIFIED BY 'your-password'"
Remember the mailuser password for when we configure postfix and dovecot later.
Creating Mail Database Tables
Neither Postfix nor Dovecot place any restrictions on the data structures you should use to support virtual mail functions. Their only requirements are that you must supply a set of queries that return specific fields as needed.
This gives you total flexibility to integrate your mail system into any arbitrary operating environment. It also means that there is no default database structure, so we must provide it ourselves!
Figure 2 below, shows the schema of our virtual mail database.
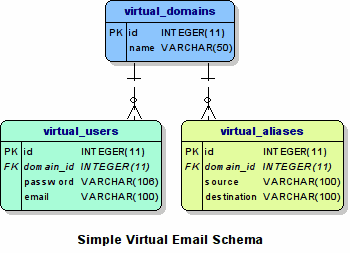
- virtual_domains - Contains an entry for each domain name served by virtual email
- virtual_users - Contains an entry for each virtual mail box served
- virtual_aliases - Maps aliases (source) to actual mail boxes (destination)
to create these tables, type
mysql --user="mailuser" -p -e "CREATE TABLE virtual_domains( id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY ( id ) );" mailserver mysql --user="mailuser" -p -e "CREATE TABLE virtual_users( id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, domain_id INT NOT NULL , password VARCHAR(106) NOT NULL, email VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY ( id ) ,FOREIGN KEY (domain_id) REFERENCES virtual_domains(id));" mailserver mysql --user="mailuser" -p -e "CREATE TABLE virtual_aliases( id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, domain_id INT NOT NULL, source VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL, destination VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY ( id ),FOREIGN KEY (domain_id) REFERENCES virtual_domains(id) );" mailserver
each time supplying the password you gave for the mysql mailuser user.
Adding Domain Entries
To add entries to the virtual_domains table using the mysql client:
mysql -p mailserver mysql> INSERT INTO virtual_domains SET id=NULL, name='my-domain.com'; quit
This table must include entries for each domain served by your virtual mail server.
You should add at least the following rows:
- The domain name - my-domain.com
- The hostname - darkstar
- The FQDN of the host - darkstar.my-domain.com
- The localhost.domain variant - localhost.my-domain.com
To see the current rows in this table using the mysql client:
mysql> SELECT * FROM virtual_domains; +----+-------------------------+ | id | name | +----+-------------------------+ | 1 | my-domain.com | | 2 | darkstar | | 3 | darkstar.my-domain.com | | 4 | localhost.my-domain.com | +----+-------------------------+
Note the automatically generated id value for the domain itself, my-domain.com, it will be used when we enter user mail boxes and mail box aliases.
Adding User Mail Box Entries
To add entries for each mail box, you will need the domain id from the previous step for the corresponding domain name.
We do not store the user passwords as plain text in the database, instead we will generate an SHA512 hash of the passwords, used by dovecot for authentication.
To insert a virtual user mailbox from the mysql client, substitute the domain id, actual password and email into the following query:
mysql> INSERT INTO virtual_users SET
id=NULL,
domain_id=1,
password=ENCRYPT('user-password', CONCAT('$6$', SUBSTRING(SHA(RAND()), -16))),
email='me@my-domain.com';
To see currently assigned mail boxes for a domain (with password column suppressed):
mysql> SELECT U.id, domain_id, email FROM virtual_domains D JOIN virtual_users U ON(U.domain_id=D.id) WHERE name='my-domain.com'; +----+-----------+-------------------+ | id | domain_id | email | +----+-----------+-------------------+ | 1 | 1 | me@my-domain.com | | 2 | 1 | you@my-domain.com | | 3 | 1 | us@my-domain.com | +----+-----------+-------------------+
To reset the password for an email user, substitute the new password and email values into this query:
mysql> UPDATE virtual_users SET
password=ENCRYPT('new-password', CONCAT('$6$', SUBSTRING(SHA(RAND()), -16)))
WHERE email='me@my-domain.com';
Adding Mail Box Alias Entries
To add entries for each mail box alias, you will again need the domain id corresponding to the domain name of the alias.
To insert a virtual mailbox alias using the mysql client:
mysql> INSERT INTO virtual_aliases SET id=NULL, domain_id=1, source='alias@my-domain.com', destination='you@my-domain.com';
In the example given, mail sent to alias@my-domain.com will be accepted and delivered to you@my-domain.com.
To see current aliases in the database:
mysql> SELECT A.id, domain_id, source, destination FROM virtual_domains D JOIN virtual_aliases A ON(A.domain_id=D.id) WHERE name='my-domain.com'; +----+-----------+---------------------+-------------------+ | id | domain_id | source | destination | +----+-----------+---------------------+-------------------+ | 1 | 1 | alias@my-domain.com | you@my-domain.com | +----+-----------+---------------------+-------------------+
Go ahead and enter a few virtual email users, and maybe an alias or two, so that you will have working accounts to test with after we set up postfix and dovecot.
For troubleshooting, use the queries shown above to verify the domains, email users and aliases in the database at any time, and to reset virtual user passwords. Return to main article page
Sources
- Originally written by astrogeek
