Table of Contents
Slackware ARM project web site | Forum | Slackware ARM development documentation | Slackware ARM installation guides
Installing Slackware on the RockPro64
| Target | |
|---|---|
| Platform | AArch64/ARM64 |
| Hardware Model | Rock Pro64 |
| Document Version | 1.04, Mar 2024 |
| Author | Stuart Winter <mozes@slackware> |
| Contributors | Brenton Earl <el0226@slackware> (R&D for the RK3399 Hardware Models) |
Video Tutorial
This tutorial is also available in video form.
Pine64 also provide unboxing and setup videos which you may find useful.
Help / Support
Please post questions to the Slackware ARM forum.
Installation Lifecycle
The Installation consists of a number of distinct stages:
- Acquiring all required hardware
- Downloading and verifying the Slackware assets
- Writing the Initialisation Bootware to the Micro SD card
- Setup of the RockPro64 hardware
- Initialising the RockPro64 with the Bootware
- Writing the Slackware Installer to the Micro SD card
- Booting the Slackware Installer
- Installing Slackware
- Completing the installation
- Booting the Slackware OS
- Post installation configuration and tweaks
Requirements
Hardware
| Item | Specification | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| RockPro64 | 2GB RAM or 4GB RAM model | - |
| RockPro64 Power Supply ('PSU') | Pine64's own | There is a cheaper alternative, but this version is recommended. Note that the link here is for the EU version - a US version is also available in the Pine64 store |
| Micro SD Card | 16GB minimum capacity, Class 10 (fast speed), good quality make | Used as Slackware's /boot partition |
| USB Multi-Card Reader | Must accept Micro SD cards | Used to write the Bootware on your host Linux computer. This isn't required if your host computer has a Micro SD card reader. |
| USB to Serial adapter | PL2303 chip. Other models may work, but this one has been tested. If your model has the option to set voltages, ensure 3volts is set! | Optional: This document covers installing using an HDMI monitor (you can find information about the Serial/UART adapter at the foot of this document), but a USB to Serial/UART adapter is recommended if you want to access the Boot Loader and Linux tty (serial line) remotely. The serial adapter is also required for developers needing to debug the boot process. |
| Jumper or Dupont cable | See images below | This is to bridge the pins required for initial firmware deployment and/or Hardware Model recovery |
| Wifi and Bluetooth module | Pine64's own | Optional |
| Heat sink and CPU fan | Pine64's own | Either a heat sink or fan are required. Some of the cases have built-in heat sinks, so check the options |
| SATA power cable | Pine64's own | Optional - depends if you use the SATA PCI card and choose to power the drives from the board (see notes below around stability) |
| Real Time Clock ('RTC') battery holder | Pine64's own | An RTC is used to keep the time when the Hardware Model is powered down. This is recommended but optional. Time can also be set via NTP once the OS has booted. |
Hardware: Storage
This table provides a list of options that have been tested with Slackware AArch64 on the RockPro64 - you only need one storage controller.
| Item | Specification | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| USB to SATA adapter | Many models will work, but this one has been tested. | For a simple installation you require either storage attached to a USB interface, or using a SATA PCIe card (see below). |
| PCIe dual port SATA 3.0 Interface Card | JMICRON+JMB582 | Recommended 2-port SATA card |
| PCIe quad port SATA 3.0 Interface Card | MZHOU / Marvell chipset | Recommended 4-port SATA card |
| SATA storage / SSD | The Kingston-SA400S37-240G has thoroughly proved itself in the Slackware ARM build infrastructure - most build machines use these, but any SSD or spinning hard disk should work | Will contain the Operating System. You can install to other storage, but this documentation covers this particular configuration only. |
Notes on storage setup
The setup documented here (2.5“ SSD connected to a USB-to-Serial adapter for power and data) has proven stable for this author.
However, powering spinning 3.5” SATA drives from the RockPro64 directly have resulted in instability of the hardware. This was resolved by powering the drives and CPU fan from an external power supply. The Slackware AArch64 primary build machines run with this power configuration and have proven stable over time.
eMMC
From the factory, your RockPro64 may contain an eMMC storage module. During the development of Slackware AArch64, it was found that the life span of these storage modules is short which makes them inappropriate for housing an Operating System. Whilst it's possible to use eMMC with Slackware, this documented installation process does not provide a supported path and the eMMC should be removed.
Computing / Network Environment
| Item | Specification | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Host Computer: an Internet-connected computer running an existing Linux distribution | The Host Computer needs approximately 5GB free storage to download the required software assets. You must be able to obtain root access to this Host computer. | This will be used to download the Slackware distribution from the Internet and write the Slackware Installer to the Micro SD card. |
Hardware Setup
In this section we'll prepare the physical aspects of the RockPro64 to receive Slackware Linux.
1. Place the computer onto a non-conductive surface ready for setup
If you have a case, install the board into it. If you do not, it should be placed onto a non-conductive surface such as plastic, wood or rubber.
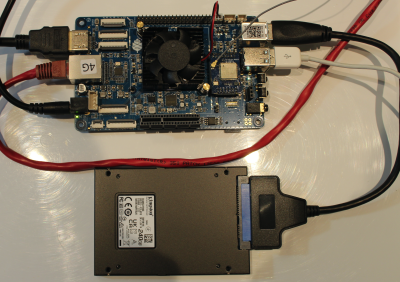
Remove eMMC storage module
In the image above you will see that the eMMC module has been removed (bottom right, left hand side of 'Head phones jack'). See the note above for the reasons behind this.
Gently prize the eMMC module from the board and store it some place safe as you may wish to experiment with it in the future.
2. Connect the peripherals
- Connect the CPU fan or heat sink
- Connect the Wifi & Bluetooth module (optional)
- Connect the storage (the image shows the USB-to-SATA adapter, but you may use the PCI card). If using the USB adapter, connect it to the blue USB3.0 port.
- Connect the Ethernet cable
- Connect the HDMI cable
- Connect the USB keyboard and mouse
The basic hardware setup is complete.
Software and Network Environment Setup
In this section, we'll prepare the Linux Host Computer to receive and download the Slackware assets required for the installation.
1. Downloading the Slackware Linux AArch64 Distribution and Installation Assets
Open a shell on the Linux Host Computer.
Prepare a directory to hold and serve the Slackware Distribution
We'll download the Slackware Linux distribution into a directory named 'slackware'.
$ cd ## returns to the root of your home directory $ mkdir slackware $ cd slackware
Determine where you are within the Host Computer's Filesystem
$ pwd /home/mozes/slackware
Installing the Slackware ARM GPG key
The Slackware ARM GPG key will be used to verify the Bootware and Slackware Installation images.
$ curl -sSL https://www.slackware.com/infra/keys/arm/GPG-KEY | gpg --import -
Set the version of Slackware AArch64 to download
At the time of writing, the only version available is 'current'.
$ SLKVER=current
Set the Hardware Model
$ HWM=rk3399_generic
Set the Internet media distribution server
If you are using a mirror server rather than the master Slackware ARM server, set it here. The format is: <hostname>::<rsync module name>
$ SLKSRV=ftp.arm.slackware.com::slackwarearm
Download the Bootware
The U-Boot Boot Loader that will be installed onto the SPI flash:
$ rsync -PavL $SLKSRV/platform/aarch64/bootware/recovery/rk3399/flash-spi-rockpro64.img.xz . $ rsync -PavL $SLKSRV/platform/aarch64/bootware/recovery/rk3399/flash-spi-rockpro64.img.xz.asc .
The Bootware (recovery/initialisation) images are approximately 400KBytes in size.
Download the Slackware Linux Installer
$ rsync -PavL $SLKSRV/platform/aarch64/bootware/installer-aio/slackwareaarch64-${SLKVER}/${HWM}.img.xz.asc slkaio.img.xz.asc
$ rsync -PavL $SLKSRV/platform/aarch64/bootware/installer-aio/slackwareaarch64-${SLKVER}/${HWM}.img.xz slkaio.img.xz
The Slackware Installer images are approximately 5 GBytes in size.
Verify the Downloads
$ gpg --verify-files *.asc
The output should be similar to this:
gpg: assuming signed data in `flash-spi-rockpro64.img.xz' gpg: Signature made Fri 27 Jan 2023 08:53:24 AM -00 using RSA key ID 1623FC33 gpg: Good signature from "Slackware ARM (Slackware ARM Linux Project) <mozes@slackware.com>" gpg: WARNING: This key is not certified with a trusted signature! gpg: There is no indication that the signature belongs to the owner. Primary key fingerprint: 36D3 7609 2F12 9B6B 3D59 A517 F7AB B869 1623 FC33 gpg: assuming signed data in `slkaio.img.xz' gpg: Signature made Thu 19 Jan 2023 08:34:27 PM -00 using RSA key ID 1623FC33 gpg: Good signature from "Slackware ARM (Slackware ARM Linux Project) <mozes@slackware.com>" gpg: WARNING: This key is not certified with a trusted signature! gpg: There is no indication that the signature belongs to the owner. Primary key fingerprint: 36D3 7609 2F12 9B6B 3D59 A517 F7AB B869 1623 FC33
Write the Initialisation Bootware to the SD Card
Slackware stores the U-Boot Boot Loader firmware within the SPI flash of the Hardware Models that use the RK3399 SoC (including the Pinebook Pro, RockPro64 et al).
In this step, we'll write the Boot Loader firmware to the same Micro SD card that will later be used to contain the Slackware Installer, and subsequently the Slackware OS' /boot partition. If you have multiple Micro SD cards available, you may prefer to use separate SD cards; but this document assumes the availability of a single Micro SD card.
Elevate yourself to root
On your Host Computer, obtain root:
$ su - ## Note the hyphen - it's required
Check what block devices are present
Prior to inserting the Micro SD Card into the USB adapter, we need to see what's already present within the OS so that we can easily locate our Micro SD card:
# lsblk -d NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINTS sda 8:0 0 465.8G 0 disk
As you can see, this Host Computer there is a single storage device - sda.
Now insert the Micro SD card into your USB Card Reader and connect the adapter to a free USB port on the Host Computer.
Run lsblk again:
# lsblk -d NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINTS sda 8:0 0 465.8G 0 disk sdc 8:32 1 58G 0 disk sdd 8:48 1 0B 0 disk
As you can see, sdc is 58GBytes in size. This is the Micro SD card (in this example, it's labeled as '64GB' on the exterior of Micro SD card).
If your Micro SD card has existing partitions, you will not see them surfaced in this list - use lsblk -b to view them.
Write the Bootware Initialisation Image to the Micro SD Card
Still as the root user, we'll switch to the directory to which the the Slackware assets have been downloaded (see earlier steps):
# cd /home/mozes/slackware/
Write the Bootware Initialisation Image to the device identified as our Micro SD card. You'll then exit the root shell, returning to your usual standard user environment:
# dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/XXX count=10 bs=1M ## Replace /dev/XXX with the correct block device (presented above by the lsblk tool) on your Host Computer # xzcat flash-spi-rockpro64.img.xz > /dev/XXX ## Replace /dev/XXX with the correct block device (presented above by the lsblk tool) on your Host Computer # sync
Remove the Micro SD card from the Host Computer
Now that we've written the Bootware Initialisation Image to the Micro SD card, you need to remove it from the Host Computer.
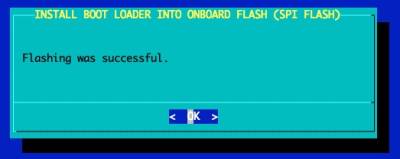
Installing the Boot Loader to SPI flash
You need to perform this one-time step to flash a Slackware version of the U-Boot Boot Loader to the SPI flash of the RockPro64.
This is required if your RockPro64 is brand new out of the box, or has previously had another Linux distribution running on it.
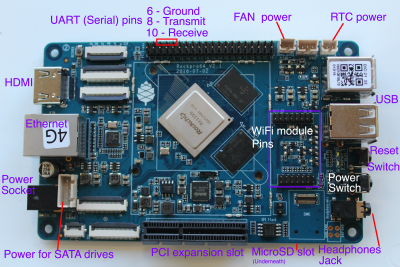
- Position the jumper/Dupont cable so that it links pin 23 (SPI_CLK_M2) and pin 25 (GND)
- Insert the Micro SD card into the RockPro64's Micro SD slot
- Connect the power to the RockPro64
- Power on the RockPro64: hold down the Power button for 2 seconds (it may also auto-power on)
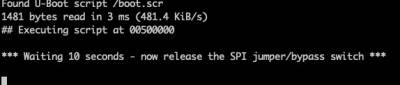
After a few seconds, you should see a message appearing on the screen - instructing you that the process will begin in 10 seconds' time.
Now remove the jumper/Dupont cable
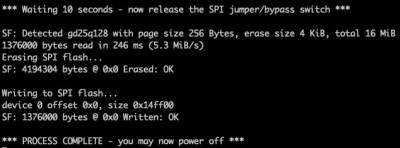
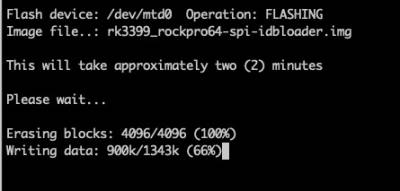
The flashing process will begin and takes approximately 1 minute to complete.
Once the process completes, hold the power button for approximately 8 seconds. The RockPro64 will power off.
Write the Slackware Installer image onto the MicroSD card
Now that the Boot Loader has been installed to the RockPro64's SPI flash, we will install the Slackware Installer image onto the same MicroSD card.
- Remove the MicroSD card from the RockPro64
- Insert the MicroSD card back into the Host Computer (as in the earlier section)
Write the Slackware Installer to the Micro SD card
Follow the instructions in the previous section to determine which block device name it occupies.
Enter the directory into which the Slackware assets were downloaded previously:
# cd /home/mozes/slackware # xzcat slkaio.img.xz | dd status=progress bs=4M iflag=fullblock of=/dev/XXX ## Substitute /dev/XXX with the correct block device # sync # exit
Remove the MicroSD card from the Host Computer
You may now disconnect the USB adapter from the Host Computer and remove the MicroSD card.
Run lsblk again to confirm that the block device assigned to the Micro SD card is no longer present:
# lsblk -d NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINTS sda 8:0 0 465.8G 0 disk
Logout from the root user
# logout
You no longer require the Host Computer.
Installing Slackware
To proceed, you must have:
- Connected the storage to the RockPro64
- Connected the HDMI monitor
- Connected the keyboard (and optionally, mouse)
- Inserted the Micro SD card containing the Slackware Installer
Encrypted storage
If you'd like to encrypt your storage, check the Disk Encryption Guide.
Begin installation
Power on the RockPro64
Press the Power Button for aproximately two seconds
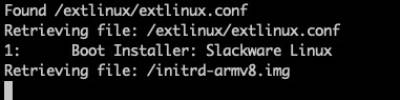
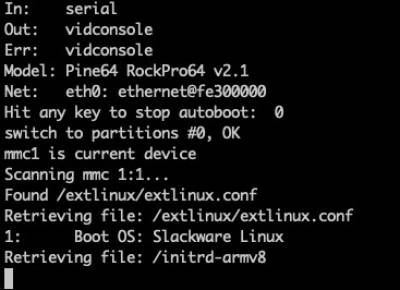
After a few seconds, the you will see the following on screen:
It takes several seconds to load and boot the installer, and it may take several seconds more for any further output to appear on the HDMI monitor. The process of obtaining an IP address via DHCP can also delay the ability to interact with the Installer.
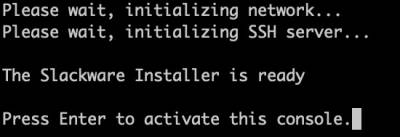
Once an IP address has been obtained, you will be presented with a prompt. Press ENTER
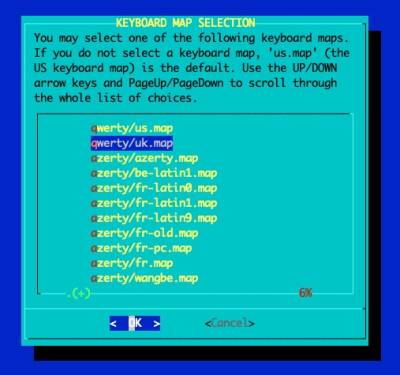
Set the keymap
Font size
If you're using a smaller monitor, such as one with a screen size less than 20 inches, it may be necessary to adjust the console font size to ensure that menus and other interface elements fit correctly on the screen. If so, type this into the shell prompt:
setfont ter-v18n
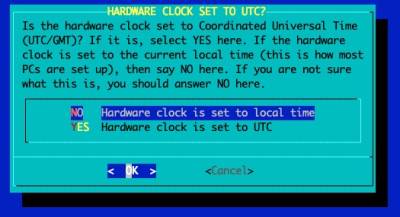
Set the date/time
Even if you have a battery pack for the RTC (Real Time Clock), the date on your system may be incorrect. We will sync the date from a highly-available NTP server:
ntpdate clock.akamai.com hwclock -w
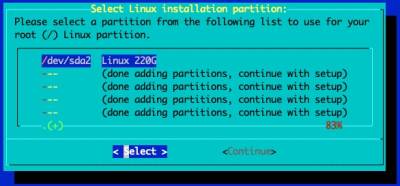
Setup disk partitions
For this installation a basic partitioning scheme will be created.
Partition
| Partition number | Device name | Size | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | /dev/sda1 | 4GB | Swap |
| 2 | /dev/sda2 | Rest of storage | OS root ('/') partition |
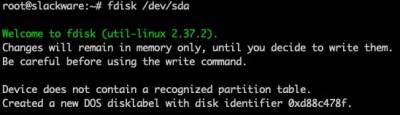
Open fdisk against the /dev/sda block device. In this guide, /dev/sda will be your primary storage, and in this guide is the SSD connected to the USB adapter.
fdisk /dev/sda
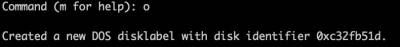
Clear an existing partition table: Press 'o' to clear the partition table
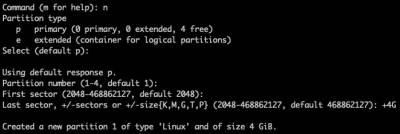
Create the Swap partition:
Type 'n' for new partition:
Type 'p' for primary partition type:
Press ENTER for the 'First sector'
Type '+4G' for the 'Last Sector'/size:
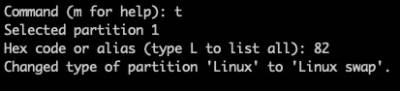
Change the partition type to 'Swap'. Type 't' then hex code '82':
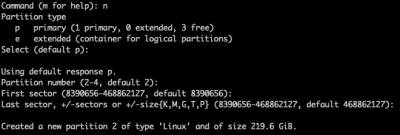
Create the partition for the root filesystem ('/'):
Type 'n' for new partition. Press ENTER to accept the defaults - this will create partition 2 as the maximum size available.
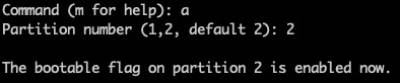
Type 'a' to mark the root partition (number 2) as bootable Type '2' to select partition 2.
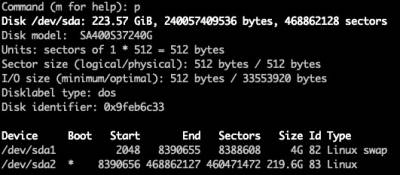
Type 'p' to print to view the partition table.
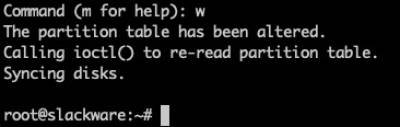
Type 'w' to write the partition table:
fdisk will now exit.
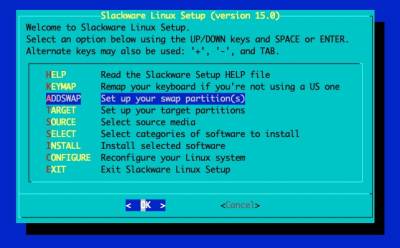
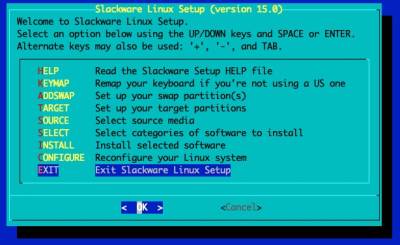
Load the Setup menu
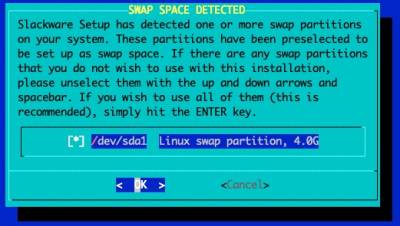
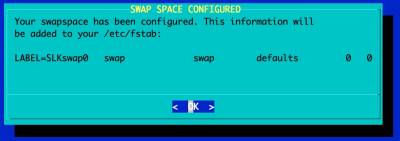
Setup Swap partition
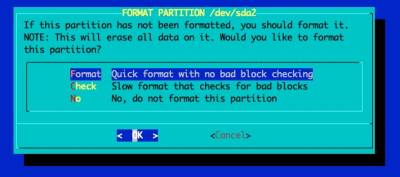
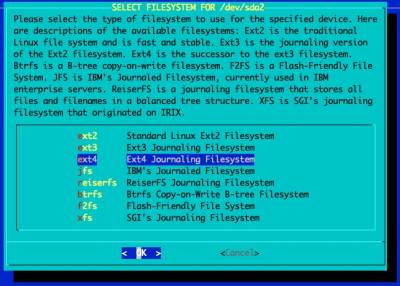
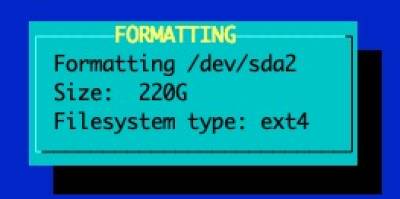
Select and format the partition for the OS' root file system
Boot Loader Configuration
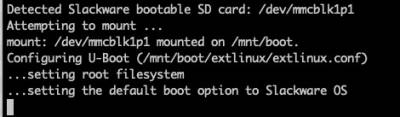
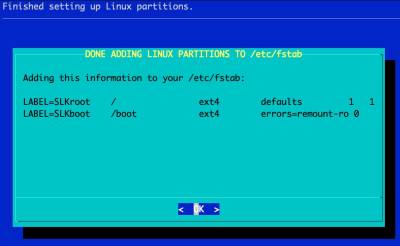
The Installer will configure the Boot Loader and the OS' /etc/fstab automatically:
The swap partitions are labeled 'SLKswap<x>', the root file system 'SLKroot', and the /boot partition 'SLKboot'.
The rationale behind this divergence is that on x86 the root file system is typically on a storage bus (SCSI, SATA, ATA), where the physical configuration (which port the storage is connected to) of the storage rarely changes. This can be the case on ARM, but it's generally to a lesser extent and the root file system may be connected to a hot-plug bus such as USB. This lends itself to the risk of device re-ordering across boot cycles (e.g. /dev/sda becomes /dev/sdb), causing boot failure.
Please be aware that the Slackware Installer only labels the swap and root file system. Therefore you are advised to manually label the file systems and modify the OS /etc/fstab accordingly. If you have only a single storage device and don't plan on adding more, you can use the settings that the Slackware Installer configures.
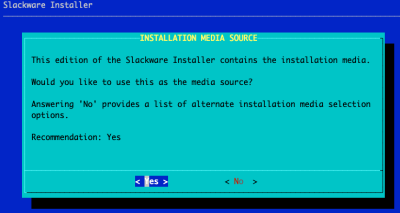
Select Source Media
Press ENTER to say 'Yes'.
If you would like to install from an alternate media source, pick 'No' and you will be presented with options to install over NFS, USB and HTTP amongst others.
Ordinarily you should always say 'Yes' unless you've been directed to do otherwise.
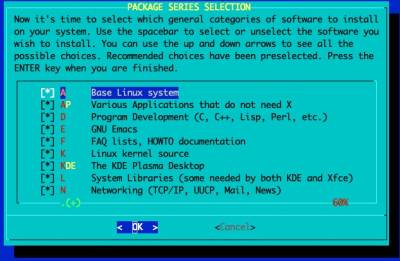
Package Series Selection
You can now choose the package sets to install. The recommendation is to install everything. A full Slackware installation will occupy approximately 15GB.
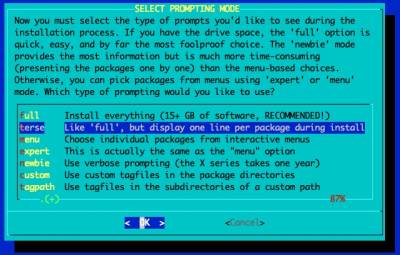
Pick the 'terse' option:
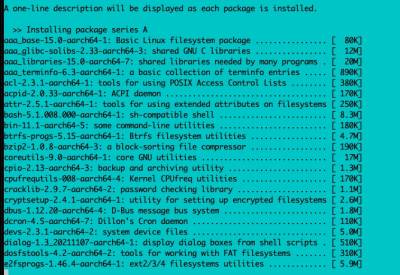
The packages will begin installing:
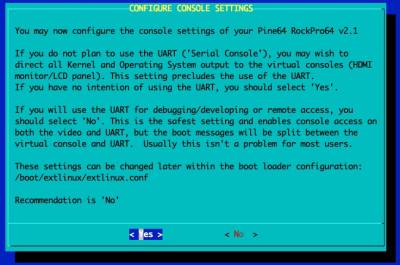
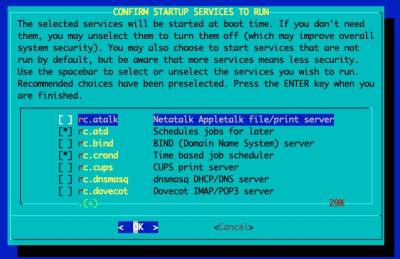
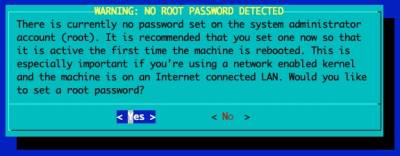
Configure the Console Settings
If you plan on using the UART/'Serial' console, you should select 'No' here. If you plan on exclusively using an HDMI monitor, you should pick 'Yes'.
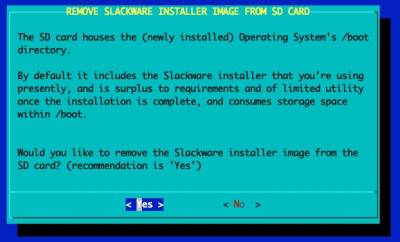
Remove the Slackware Installer from the SD card
The Micro SD card is transformed from being the Slackware Installer into the Slackware OS's /boot partition. At this stage, if the installation has worked for you (at certain points in the Slackware installer you are past the point of no return) you can delete the Installer. However, if something has gone wrong you can reset the RockPro64 and reboot the installer without having to re-deploy the Slackware Installer image from your Linux Host Computer.
Generally you should say 'Yes' here.
Install the Boot Loader to SPI flash
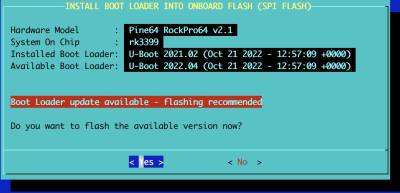
The initial Boot Loader flash performed earlier in these instructions typically contains an older version of the Boot Loader, where as the version packaged within the Installer contains the most recent version.
When an upgrade is required, in most cases you'll see a screen like this which provides information about the currently installed Boot Loader and the newer version available:
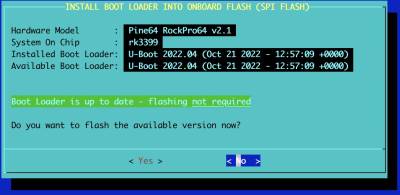
If the installed Boot Loader matches the currently available version, you will be advised that flashing is unnecessary. However, you can re-flash it if you wish.
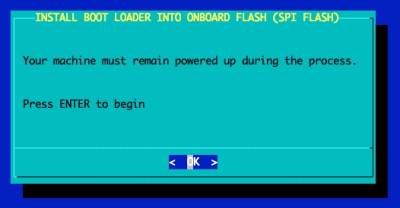
If you proceed with flashing, the work flow looks like this and takes approximately two minutes to complete.
Post Installation Configuration
The Slackware Installer will walk you through the standard Slackware setup. The on-screen instructions will suffice.
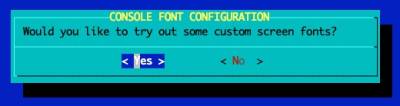
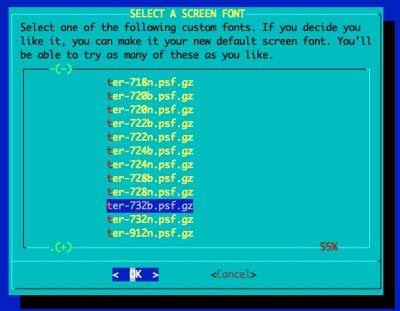
Select a Console Font
It's recommended for the RockPro64 and Pinebook Pro that a larger console font is configured.
The recommended font is 'ter-732b.psf'. This is the font used within the Installer.
Continue Post Installation Configuration
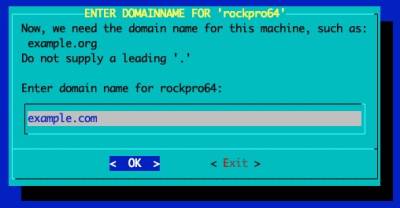
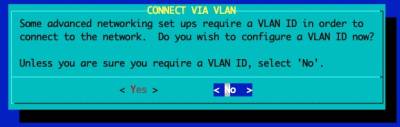
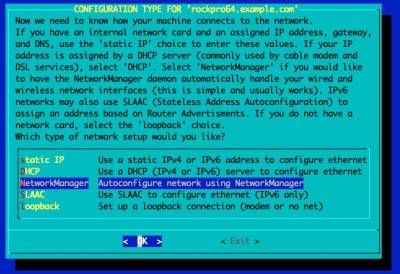
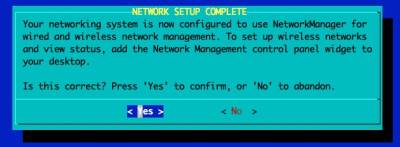
Configure GUI Window Manager
Continue Post Installation Configuration
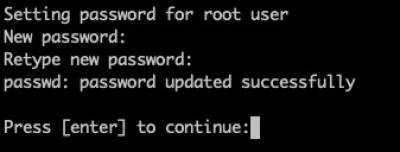
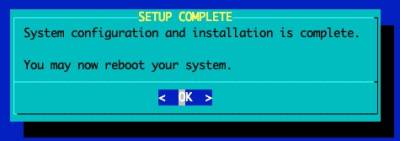
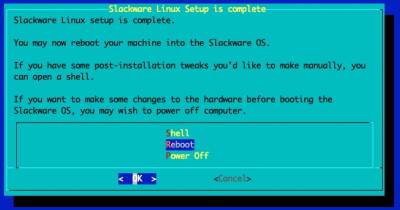
Slackware Setup Complete
Generally you'll want to reboot into the OS.
However, if you are planning on setting up RAID or need to customise the Operating System Initial RAM Disk, you should select 'Shell'.
The Slackware OS will be found within '/mnt'. You can use the 'os-initrd-mgr' tool (Video tutorial).
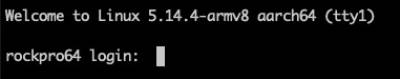
Booting the Slackware OS
Login to the Slackware OS
Post Installation Configuration
There are a few post-installation configuration tasks to complete.
Add a plebeian user
You should add a plebeian (non-root) user using the 'adduser' tool.
This is documented here.
CPU fan speed
The CPU fan speed is controlled statically during boot.
By default it'll set the speed to '65' which is the lowest speed. If you want to change this:
As root, edit the Hardware Model run control configuration file:
# vi /etc/rc.d/rc.platform.conf # or substitute 'vi' for your favourite editor
Within that configuration you'll find examples. Un-comment and set accordingly and reboot.
If you do not have a fan (typically you'll have a heatsink instead) you can also disable the fan. Within the config file uncomment the variable CPU_FAN_OFF=Yes.
NTP (Network Time Protocol) setup
If your RockPro64 does not have an RTC battery backup, you may wish to configure it to set time from an NTP Server.
Managing Slackware on the RockPro64
Keeping the Slackware OS up to date
One of the preferred tools to keep your system up to date is slackpkg.
Loading Additional Linux Kernel Modules within the OS Proper
Often Kernel modules for discovered hardware will be automatically loaded, but occasionally you will need to manually configure the loading of some modules.
/etc/rc.d/rc.modules.local
This file is a shell script that is run as one of the last steps before the OS has fully booted. You can enter modprobe commands here to load the specific modules you require.
Configuration files within the directory /lib/modprobe.d/ can be used to configure the parameters of the modules. Existing files within that directory serve as reference examples should you need them.
Loading Additional Linux Kernel Modules early in the boot sequence
There are a number of peripherals that may require Kernel modules loading early on in the boot sequence. An example of this would be RTCs (Real Time Clocks) or storage controllers that are required to access the file systems on which the OS lives.
To load Kernel modules during the early boot sequence, read:
/boot/local/README.txt
As root, the easiest way to begin is by renaming the example script:
mv /boot/local/load_kernel_modules.post.sample /boot/local/load_kernel_modules.post
Then add the appropriate module loading commands to: /boot/local/load_kernel_modules.post
You can also add shell code here to initialise a peripheral - writing something to the peripheral's Kernel interface, for example.
Use a graphical login manager
If you prefer to use a graphical login manager, you can configure the default runlevel as 4:
su - sed -i 's?id:3:?id:4:?g' /etc/inittab reboot
Slackware repository partition
The Slackware Installer image contains a type ext4 partition labeled SLKins_aio-pkgs from which the packages are installed.
root@slackware:~# mount LABEL=SLKins_aio-pkgs /mnt/zip root@slackware:~# cat /mnt/zip/README.txt This file system contains the Slackware repository that is used during the installation of Slackware. Once you've booted into your OS you can delete or change this partition if you wish, or perhaps you might like to retain it for future reference. root@slackware:~#
Customising the Slackware Linux Kernel
If you'd like to customise the Linux Kernel, the easiest way is to follow the HOWTO guide and use the Slackware ARM Kernel build script to create new packages.
Reducing Boot Time
Slackware ARM ships with a generic OS InitRD (Operating System Initial RAM Disk - the environment that prepares the machine to boot the Operating System Proper), so as to support a wide range of Hardware Models.
However, this isn't the optimal setup once the Slackware OS has been installed because the generic OS InitRD typically exceeds 250MB, which in some cases can add several seconds to the boot time whilst it's loaded from the SD card.
The os-initrd-mgr (Operating System Initial RAM Disk Manager) tool has an option to synchronize the OS InitRD's Kernel modules with only those presently loaded within the Operating System.
To do this:
$ su -c 'os-initrd-mgr --sync-loaded-kmods' - # note the final -
a/kernel-modules package before a/kernel. If not, it'll revert to the generic OS InitRD until you next reboot.
If you are using slackpkg to manage upgrades, this is handled for you.
This option isn't the default, but you can make it so by following the instructions within /etc/os-initrd-mgr.conf.sample
This way when you upgrade the Kernel packages in the order described above, it'll automatically synchronize the modules.
For example, when running Linux 5.17.1, upgrading to 5.17.2 will work; but an upgrade of Linux 5.17.1 → 5.18.1 will require a reboot then to run os-initrd-mgr again to re-sync.
a/kernel package (and unset the setting if you configured it in /etc/os-initrd-mgr.conf).
Installing extra Software
Slackware comes with a good base of software applications, but there are plenty more available in the Open Source Ecosystem.
The best way to add new software is to use the build scripts from SlackBuilds.org.
Managing the Boot Loader firmware
During the Slackware installation process, you are offered the opportunity to flash the Boot Loader to the SPI flash. Occasionally, updates will be made available to the Boot Loader to address bug fixes and provide improvements.
Slackware provides a package hwm-bw-rk3399 within the a series that contains the latest Boot Loader firmware and contains the bootloader-flash-rk3399 tool to manage the upgrade life cycle.
Upgrading the Boot Loader firmware
- Upgrade to the latest available version of the package
hwm-bw-rk3399(usingslackpkgas described within this document). - As root, run the
bootloader-flash-rk3399tool.
In this example we'll run the Boot Loader management tool as the root user using the su tool:
$ su -c 'bootloader-flash-rk3399' - # You must include the trailing '-' character
When an upgrade is required, in most cases you'll see a screen like this which provides information about the currently installed Boot Loader and the newer version available:
If you've wiped the Boot Loader from SPI flash or have installed a non-Slackware firmware build, you will see a screen like this where the existing installed Boot Loader is unrecognised:
If the installed Boot Loader matches the currently available version, you will be advised that flashing is unnecessary. However, you can re-flash it if you wish.
If you proceed with flashing, the work flow looks like this and takes approximately two minutes to complete.
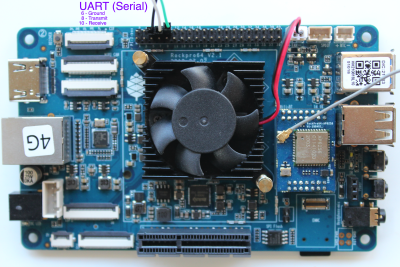
Using the Serial/UART adapter
This documentation discusses using the RockPro64 without the UART/Serial console.
If you'd like to use one, there are two that have been tested.
USB Serial Device converter: Prolific Technology Inc / PL2303
This image below shows the PL2302 (the Serial adapter listed in the Hardware table at the head of this document) connected to the RockPro64:
USB Serial Device converter: FTDI / FT232RL
This is the model shown here.
Using the USB Serial Device converter on the Linux Host Computer
Once wired up, connect the USB end of the adapter into your Linux Host Computer, and use the following command.
/dev/ttyUSB0. If so, you will need to adjust the device name accordingly (e.g. perhaps /dev/ttyUSB1).
screen -T screen-256color /dev/ttyUSB0 1500000
Known bugs and limitations
None presently.
Supporting the Slackware ARM project
Maintenance of the Slackware ARM port takes not only a lot of time, but also has financial costs such as the on-going use of electricity, Internet hosting and purchasing and maintenance of ARM hardware.
Once you find yourself enjoying using the ARM port of Slackware, please take a few moments to show your appreciation through sponsorship.
Contributing to the Slackware ARM project
There are a plethora of ARM devices on the market which requires initial R&D and continuous testing. If you'd like to help Slackware support more ARM boards, please check out the documentation explaining how to get involved.